Z-Scheme MoS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction for efficient visible light photocatalytic CO2 reduction†
Abstract
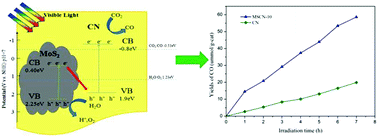
Z-Scheme MoS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalysts were fabricated using a hydrothermal deposition procedure together with a calcination route, and then applied for CO2 photoreduction. Experimental results indicated that the 10% MoS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction displayed the best photocatalytic performance. Furthermore, the maximum CO yields of 58.59 μmol (g-cat)−1 under 7 h-visible light irradiation was up to 2.94 times that of the unadulterated g-C3N4. The enhanced photocatalytic performance of 10% MoS2/g-C3N4 catalyst was due to the favored visible light response, the efficient separation of photogenerated electron–hole pairs as well as its larger specific surface area.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...