The first investigation of europium silicate melilite for second-order nonlinear optical application: experimental and theoretical studies†
Abstract
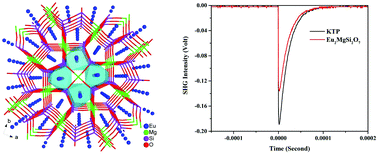
A europium pyrosilicate, Eu2MgSi2O7 (1), is obtained using a high-temperature solid-state reaction. It crystallizes in the tetragonal noncentrosymmetric space group P![[4 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0034_0304.gif) 21m, and its structure features a 2D structure built by SiO4 and MgO4 tetrahedra, resulting in interlayer cavities occupied by Eu2+ ions. It has a SHG intensity around 0.7 times that of KTP in the particle size range of 45–75 μm under 2.1 μm radiation, demonstrating a relatively strong effect among the silicates. A typical photoluminescence phenomenon of Eu2+ can be observed at 482 nm. Calculations on the electronic structure and optical properties of 1 are performed. Moreover, to discuss the potential of pyrosilicates and related compounds as NLO crystals, the theoretical analysis on other A2BM2O7 compounds is also addressed.
21m, and its structure features a 2D structure built by SiO4 and MgO4 tetrahedra, resulting in interlayer cavities occupied by Eu2+ ions. It has a SHG intensity around 0.7 times that of KTP in the particle size range of 45–75 μm under 2.1 μm radiation, demonstrating a relatively strong effect among the silicates. A typical photoluminescence phenomenon of Eu2+ can be observed at 482 nm. Calculations on the electronic structure and optical properties of 1 are performed. Moreover, to discuss the potential of pyrosilicates and related compounds as NLO crystals, the theoretical analysis on other A2BM2O7 compounds is also addressed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...