Selective separation of cadmium(ii) from zinc(ii) by a novel hydrophobic ionic liquid including an N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-methylpyridyl)-1,2-phenylenediamine-4-amido structure: a hard–soft donor combined method†
Abstract
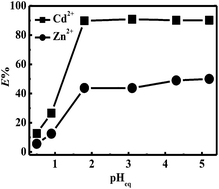
A novel hydrophobic ionic liquid including an N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-methylpyridyl)-1,2-phenylenediamine-4-amido structure ((IL-1,2-tpbd)+NTf2−) was successfully synthesized. (IL-1,2-tpbd)+NTf2− combined one amido (O-hard donor) and four pyridine (N-soft donor) groups. Its Cd2+ and Zn2+ separation behavior in nitric acid solution was investigated as a function of the extraction time, effect of pH etc. by dissolving (IL-1,2-tpbd)+NTf2− in a room temperature ionic liquid, 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ((C6mim)+NTf2−). The extraction kinetics were fairly fast and could reach equilibrium within 4 h. When pHeq ≥ 1.8, the extraction percentage of Cd2+ and Zn2+ remained constant and the maximum separation factor was calculated as 12.78 at pHeq = 3.1; when pHeq < 1.8, the extraction percentage of Cd2+ and Zn2+ decreased drastically due to the protonation of the pyridine groups. Complete stripping of the extracted Cd2+ and Zn2+ from the ionic liquid phase into an aqueous phase was successfully achieved under highly acidic conditions ([HNO3] = 2 M) without adding any other metal complex forming agents. The extraction mechanism was summarized as a cation exchange due to the independence of nitrate ions in the extraction process. Additionally, the results of the slope analysis and UV-vis titration revealed the formation of a 1 : 2 complex. Furthermore, (IL-1,2-tpbd)+NTf2− showed a higher preference for Cd2+ even under the interference of various co-existing metal ions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...