NIXANTPHOS: a highly active ligand for palladium catalyzed Buchwald–Hartwig amination of unactivated aryl chlorides†‡
Abstract
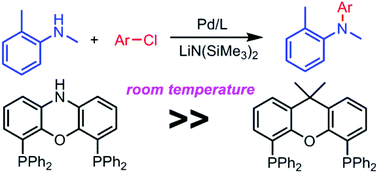
Xantphos is one of the two most common ligands used in palladium catalyzed Buchwald–Hartwig amination reactions, because of its broad scope and high probability of success. It does not, however, work well with unactivated aryl chlorides. Herein NIXANTPHOS is compared to Xantphos and an array of mono- and bidentate phosphines. NIXANTPHOS outperforms Xantphos and all other bidentate ligands examined. Under the optimal reaction conditions, unactivated aryl chlorides afford the expected products in good to excellent yield with as low as 0.05 mol% (500 ppm) palladium loading.
- This article is part of the themed collection: In celebration of Richard Andersen’s 75th birthday


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...