Dual-acting antitumor Pt(iv) prodrugs of kiteplatin with dichloroacetate axial ligands†
Abstract
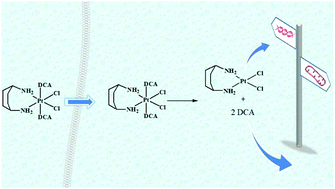
With the aim to obtain dual acting drugs able to target both nuclear DNA and mitochondria, Pt(IV) kiteplatin derivatives having dichloroacetate (DCA) ligands in axial positions have been synthesized. The rather fast hydrolysis (t1/2 of ca. 1 h) and reduction (by ascorbic acid) of these Pt(IV) derivatives did not impede a potent pharmacological effect on tumor cells. Moreover, similarly to kiteplatin, also the Pt(IV)-DCA compounds proved to be capable of overcoming oxaliplatin-resistance, which is particularly important in view of the fact that metastatic colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer in males and the second in females. The possible role of DCA released by the Pt(IV) compounds in eliciting the antiproliferative activity has also been investigated. Pt(IV)-DCA compounds determine a substantial increase of ROS production, blockage of oxidative phosphorylation, hypopolarization of the mitochondrial membrane, and caspase-3/7 mediated apoptotic cell death.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...