Water-soluble platinum nanoparticles stabilized by sulfonated N-heterocyclic carbenes: influence of the synthetic approach†
Abstract
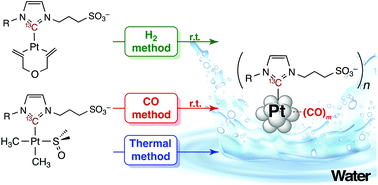
The synthesis of metal nanoparticles (NPs) under controlled conditions in water remains a challenge in nanochemistry. Two different approaches to obtain platinum NPs, which involve the treatment of aqueous solutions of preformed sulfonated (NHC)Pt(II) dimethyl complexes with carbon monoxide, and of (NHC)Pt(0) diolefin complexes with dihydrogen (NHC = N-heterocyclic carbene), are disclosed here. The resulting NPs were found to be highly stable in water under air for an indefinite time period. Coordination of the NHC ligands to the platinum surface via the carbenic carbon was monitored by solid-state NMR spectroscopy, and the presence of a platinum–carbon bond was unambiguously evidenced by the determination of a 13C–195Pt coupling constant (1106 and 1050 Hz for NPs containing 13C labeled-NHC ligands and prepared under CO and H2, respectively). The coordination of CO to the (NHC)Pt(II) precursors prior to formation of the NPs was confirmed by NMR spectroscopy. When using a disulfonated NHC ligand, a second coordination sphere containing bis(NHC)Pt(II) complexes is described. Under CO, the formation of NPs was found to be slower than in a previously reported thermal method (Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 13220–13224), but led to NPs of similar sizes, whereas under H2, the synthesis of platinum NPs progressed even more slowly and produced larger NPs. In addition to the influence of the synthetic approach, the present study highlights the importance of ligand design for NP stabilization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...