The mechanism of manganese dissolution on Li1.6Mn1.6O4 ion sieves with HCl†
Abstract
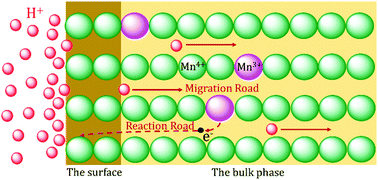
Li1.6Mn1.6O4 is a representative ion sieve material that is used to recover lithium from salt brines and bitterns owing to its high lithium ion adsorption capacity reaching 11.9–44 mg g−1. However, manganese dissolution during acid treatment hinders the industrial application of the material. For investigating the mechanism of manganese dissolution, the precursor Li1.6Mn1.6O4 and ion sieve H1.6Mn1.6O4 were prepared and characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), chemical content analyses, diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier-transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results of XRD, SEM, and FT-IR showed that the bulk phase of Li1.6Mn1.6O4 retained the spinel structure, whereas the lattice diminished during acid treatment. The results of chemical content analyses showed that the bulk phase of Li1.6Mn1.6O4 contained a few trivalent manganese atoms and that the mean valence of manganese in the material increased during acid treatment. DRIFTS and XPS exhibited that the surface of Li1.6Mn1.6O4 was mostly full of tetravalent manganese and retained the spinel structure during acid treatment. In the proposed mechanism of manganese dissolution, an electron of trivalent manganese in the bulk phase transfers to the surface and is captured by tetravalent manganese within the acidic environment. Then, tetravalent manganese is converted to bivalent manganese after acquiring sufficient electrons, and dissolution occurs simultaneously.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...