Hydrogenated Cu2O\Au@CeO2 Z-scheme catalyst for photocatalytic oxidation of amines to imines†
Abstract
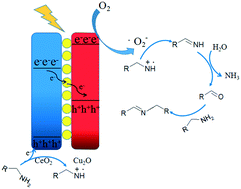
The design and fabrication of highly active visible light photocatalysts for organic synthesis reactions are particularly challenging for solar energy utilization and conversion. Herein, hydrogenated Z-scheme yolk–shell Cu2O\Au@CeO2 (H–Cu2O\Au@CeO2) photocatalysts were synthesized using cubic Cu2O as the starting core material via surface Au deposition and oxidation etching process, followed by hydrogenation treatment. When compared with CeO2, Cu2O@CeO2, and Cu2O@CeO2\Au nanocomposites, optimized H–Cu2O\Au@CeO2 showed remarkably higher visible light oxidation activity for the synthesis of imines from amines at ambient pressure and room temperature. The remarkably enhanced photoactivity of the H–Cu2O\Au@CeO2 composite mainly derives from the enhanced photoinduced charge separation efficiency, porous yolk–shell structure, proper surface defects, and well-maintained strong oxidation/reduction capabilities. The Z-scheme charge transfer process and photocatalytic reaction mechanism of the H–Cu2O\Au@CeO2 composites were also provided through spectral and photoelectrochemical analyses together with the investigation of structure and photocatalytic oxidation reactions. This study provides a probable approach for designing unique Z-scheme catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...