The sustainable heterogeneous catalytic reductive amination of lignin models to produce aromatic tertiary amines†
Abstract
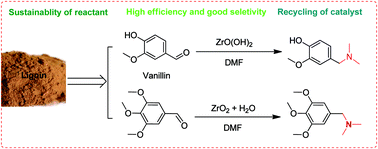
A novel heterogeneous catalytic process for efficient reductive amination is developed in the presence of heterogeneous zirconium-based catalysts, in which N,N-dimethylformamide is used as the solvent, low-molecular-weight amine source and reductant. Aromatic tertiary amines have been produced from lignin-derived aromatic aldehydes via the mild Leuckart reaction with ZrO2 or ZrO(OH)2 as catalysts, for instance, a 95.8% yield of N,N-dimethyl-1-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)methanamine in a 100% selectivity is obtained from the reductive amination of 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzaldehyde under mild conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...