In vitro evolution of an l-amino acid deaminase active on l-1-naphthylalanine†
Abstract
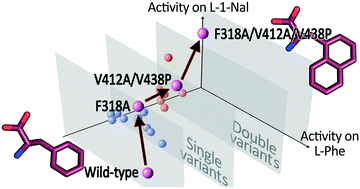
L-Amino acid deaminase from Proteus myxofaciens (PmaLAAD) is a promising biocatalyst for enantioselective biocatalysis that can be exploited to produce optically pure D-amino acids or α-keto acids. In this study, we improved the catalytic efficiency of PmaLAAD on L-1-naphthylalanine (L-1-Nal), a synthetic amino acid of biotechnological interest. Eight evolvable positions were identified by a molecular docking and evolutionary conservation analysis. These positions were subjected to site-saturation mutagenesis, producing “smaller but smarter” libraries of variants. The best variant (F318A/V412A/V438P PmaLAAD) possesses a ∼5-fold lower Km (0.17 mM) and a ∼7-fold higher catalytic efficiency (9.2 s−1 mM−1) on L-1-Nal than the wild-type enzyme. Molecular docking analysis suggests that the substitutions increase the active site volume, allowing better binding of the bulky L-1-Nal substrate. Bioconversion reactions showed that the F318A/V412A/V438P PmaLAAD variant outperforms the wild-type enzyme in the deracemization of D,L-1-Nal: the complete conversion of 0.6 mM of the L-enantiomer was achieved in about 15 min, which is ∼7.5-fold faster than the wild-type enzyme. In addition, the F318A/V412A/V438P PmaLAAD is efficiently employed, together with the M213G D-amino acid oxidase variant, to produce 1-naphtylpyruvate from racemic D,L-1-Nal in one pot.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...