Cobalt lactate complex as a hole cocatalyst for significantly enhanced photocatalytic H2 production activity over CdS nanorods†
Abstract
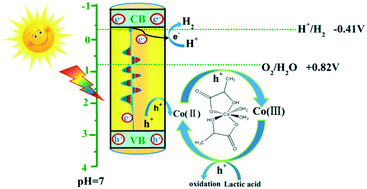
Photocatalytic water splitting has been widely investigated in recent years, and most of the catalysts depend strongly on noble metal co-catalysts which are scarce and expensive. Herein, we report a noble metal free system using CdS nanorods as a photocatalyst and a cobalt lactate complex as a cocatalyst. Under visible light irradiation, a H2 evolution rate of 15.59 mmol h−1 g−1 is obtained when the CdS and cobalt lactate complex are used for photocatalytic water splitting; this rate is 3 times that obtained with a Pt/CdS photocatalyst. Moreover, the stability of CdS is also obviously improved using a cobalt lactate complex as a cocatalyst. The origin of the improved photoactivity is investigated by a variety of controlled experiments. The results show that the cobalt lactate complex as a hole acceptor inhibits the recombination of photo-generated electrons and holes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...