Ionic liquids-coordinated Au catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination: DFT approach towards reaction mechanism and adsorption energy†
Abstract
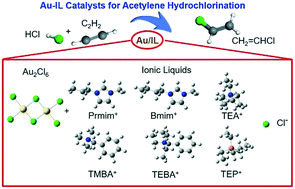
In this study, the addition of various ILs to a Au catalytic system for acetylene hydrochlorination reaction was explored via density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The most common IL cations including imidazolium IL cations, quaternary ammonium IL cations and quaternary phosphonium IL cations were selected and compared. The reaction pathways were explored and the corresponding activation energies were obtained. Furthermore, adsorption energies of each reactant and product were also calculated, which was crucial for predicting the performance of the catalysts. It was found that IL addition can significantly change the energy profiles in the reaction pathways and the adsorption energies of each reactant and product, indicating the capacity of ILs for tuning the catalytic properties of Au catalysts in this reaction. Experimental activation energies were also obtained and the data were compared with DFT results. The consistency of computational and experimental results provides valuable instructions for the design and preparation of high performance non-mercury catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...