Au–Pd NPs immobilised on nanostructured ceria and titania: impact of support morphology on the catalytic activity for selective oxidation†
Abstract
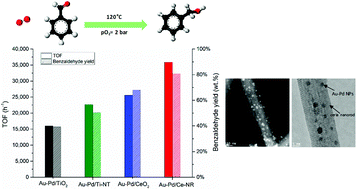
Bimetallic Au–Pd nanoparticles supported on different ceria and titania nanostructures have been prepared by sol-immobilisation, and evaluated in the solvent-less selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. The catalysts were characterised by TEM, STEM, XRD, XPS, ICP-AES, and nitrogen adsorption–desorption measurements. The activity of the catalysts was found to be strongly related to the morphology, structure and physiochemical properties of the supports. Au–Pd/ceria nanorods exhibited remarkably high catalytic activity (TOF > 35 900 h−1), and was found to be considerably more active than Au–Pd/titanate nanotubes, and Au–Pd catalysts supported on conventional ceria and titania nanopowders. The outstanding catalytic performance of Au–Pd/ceria nanorods is attributed to the unique surface chemistry of ceria nanorods, and the ability of catalyst preparation method (i.e. sol-immobilisation) to control the metal particle size and the bimetallic alloy formation. The presence of surface defects and high concentration of oxygen vacancies and Ce3+ in ceria nanorods is likely responsible for the stabilisation of Au–Pd NPs during sol-immobilisation, which led to a very small mean particle size (2.1 nm) corresponding to a dispersion of approximately 52%, and a high surface metal concentration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...