Morphology and dispersion of nanostructured manganese–cobalt spinel on various carbon supports: the effect on the oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media†
Abstract
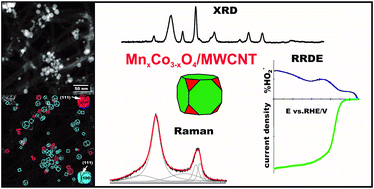
In this work a model nanometric manganese–cobalt spinel was deposited on five selected carbon carriers (Vulcan XC-72, Printex85, multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), mesoporous carbon CMK-1, and amorphous carbon C-am.) to examine their role in modifying the electrocatalytic properties of the supported active phase for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in alkaline media. The synthesized materials were thoroughly characterized by scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Raman spectroscopy (RS). The results confirmed the formation of a highly crystalline nanometric manganese–cobalt spinel and allowed for assessment of an amorphous phase content in the carbon supports used. The composition of the obtained catalysts was investigated by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) measurements. The electrocatalytic properties of the supported spinels were determined by the rotating disk electrode (RDE) and the rotating ring disk electrode (RRDE) methods and compared with those of a commercial platinum catalyst (20 wt% Pt/Vulcan XC-72). STEM analysis revealed that the carbon support governs both the dispersion and the morphology of the deposited spinel. In the case of mesoporous and amorphous carbon supports, the spinel nanocrystals exhibit a polyhedral shape with almost equal abundance of the (111) and (100) facets. The shape of the spinel nanocrystals deposited on the Vulcan XC-72 and Printex85 supports is dominated by the (111) termination, whereas for the MWCNT support the (100) facet is the most abundant accompanied by the highest dispersion of the nanoparticles. Electrochemical studies of the ORR revealed that the amorphous phase fraction in the carbon support promotes 2e− reduction, leading to production of HO2−. This undesired pathway is inhibited by preferential exposition of the (100) facets. The superior performance of the MWCNT support in the 4e− reduction process results from three factors: lowest content of the amorphous component, best dispersion of the spinel active phase, and its ability to promote preferential (100) faceting of the nanocrystals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...