Multianalytical approach for surface- and tip-enhanced infrared spectroscopy study of a molecule–metal conjugate: deducing its adsorption geometry
Abstract
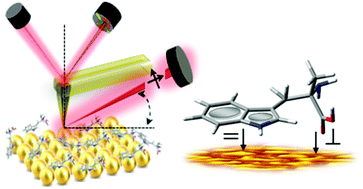
This study presents a multianalytical approach for surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy (SEIRA) and tip-enhanced infrared nanospectroscopy (TEIRA) studies of the α-methyl-DL-tryptophan adsorption geometry on a gold nanoparticle surface. Comparison of SEIRA spectra obtained in the transmission, attenuated total reflection and reflection modes verified the reproducibility of the adsorption. The application of the AutoSeagull (Harrick Scientific) accessory enabled us to track the dependence of the incident angle on the relative band intensity in the same area of the sample. Furthermore, the effect of two polarization modulations (p and s) in TEIRA was examined to deduce the adsorption geometry and to better understand the molecule/metal interaction. The nanogap between a gold-coated atomic force microscopy (AFM) tip and the gold surface induced electromagnetic enhancement in the optical field intensity. This is associated with the additional near-field electromagnetic field trapping effect. The local field intensity reinforcement significantly increased the infrared absorption cross-section of the compound under the tip with simultaneous improvement in spatial resolution. The originality of this study lies in the combination of various measurement modes and incident angles in SEIRA and two orthogonal polarizations in TEIRA to provide comprehensive characterization of the adsorption phenomenon. The results give important insights into tracking subtle changes in molecule geometry upon adsorption.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...