Ion fluctuations and intermembrane interactions in the aqueous dispersions of a dialkylchain cationic surfactant studied using dielectric relaxation spectroscopy and small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering†
Abstract
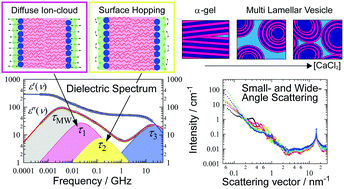
A dialkylchain cationic surfactant forms the so-called α-gel in water showing virtually no fluidity, which is transformed into a highly fluidic dispersion upon addition of a small amount of salt. This intriguing phenomenon is utilized in household industries. However, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we use dielectric relaxation spectroscopy (DRS) and simultaneous small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering (SWAXS) to shed light on this issue. We find that an excess amount of CaCl2 induces an α-gel-to-multi-lamellar vesicle (MLV) transition accompanied by a marked increase of the reservoir volume fraction. This resembles an unbound lamellar-to-bound lamellar transition that cannot be explained without invoking a weak long-ranged electrostatic attraction. The DRS data provide evidence that the counterions fluctuate both vertically and laterally at the interface, whose relaxation amplitudes sharply depend on a percolating state of an aqueous phase. The strikingly small bulk-water amplitude is likely to reflect depolarizing electric fields induced by the MLV architecture, along with genuine hydration effects. The modified Caillé approach to the SAXS intensities reveals sensitive salt-concentration dependent membrane–membrane interactions. The least undulating membranes are formed at a salt concentration of ca. 10 mmol L−1. Above 25 mmol L−1, where small surface separation (<2.5 nm) is attained, far more undulating membranes than those predicted by the Helfrich interaction are produced. This suggests that the hydration forces, generally believed to induce strong short-range repulsion, do not suppress the membrane undulation fluctuations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...