Effective lead optimization targeting the displacement of bridging receptor–ligand water molecules†
Abstract
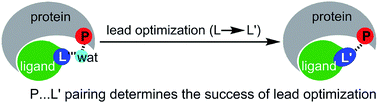
Enhancing the binding affinities of ligands by means of lead modifications that displace bridging water molecules at protein–ligand interfaces is an important and widely studied lead optimization strategy. However, it is still challenging to ensure the success of this lead optimization strategy. Here we use theoretical derivations, which are then validated using reported experimental data, to identify the major determining factors in lead optimization designed to displace bridging water molecules. Our findings demonstrate that the nature of hydrogen-bond pairing between the ligand and protein polar atom(s) is the principal factor displacing interface water molecules, and not the binding strength of the water molecule. Our results also indicate that all interfacing bridging water molecules can potentially be targeted for displacement using this new approach. In summary, we show that strong–strong/weak–weak hydrogen-bond pairings of ligand atoms with protein atoms may provide useful guidance in lead modifications by designing modified ligands with higher binding affinities than their lead molecules. This study can help to increase the efficiency of rational drug design.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...