How an electric field can modulate the metal ion selectivity of protein binding sites: insights from DFT/PCM calculations
Abstract
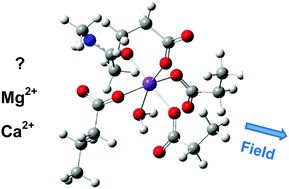
Selecting the “right” metal cation from the surrounding intracellular/extracellular fluids is of crucial importance for proper functioning of metalloproteins. Over the course of a few billion years of cell evolution various strategies have been developed by the host protein or cell machinery to secure the most favorable conditions for cognate cation binding. The effect of internal/external electric fields, potentially capable of influencing the process of metal selectivity in proteins, however, remains an enigmatic and unexplored area of research. Several outstanding questions remain unanswered: (1) Can, and if so, to what extent, an electric field affect the competition between different metal species for protein ligands? (2) What type of binding sites (with specific architecture, polarizability, and solvent exposure) are more susceptible to electric stimuli? (3) How do the basic parameters of the electric field – its strength and directionality – modulate the selectivity of the metal binding site? (4) What is the upper limit of the electric field magnitude that preserves the integrity of the metal binding site? Here, by employing density functional theory calculations combined with continuum dielectric method computations, we endeavor to shed light on these questions by studying the thermodynamic outcome of the competition between Mg2+ and Ca2+ in a model EF-hand motif metal binding site under the influence of a dipole electric field with variable magnitude and directionality. The calculations reveal that the electric field (either internal or external) is a potent force that can modulate the metal selectivity of the binding site and thus can be added to the list of factors governing the metal competition in metalloproteins. An oriented external electric field with a particular directionality could be used as a switch to enhance or attenuate the preference of the binding site toward given metal species.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...