Ab initio design of light absorption through silver atomic cluster decoration of TiO2†
Abstract
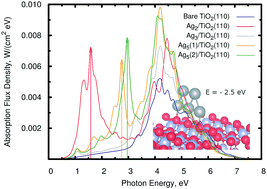
A first-principles study of the stability and optical response of subnanometer silver clusters Agn (n ≤ 5) on a TiO2(110) surface is presented. First, the adequacy of the vdW-corrected DFT-D3 approach is assessed using the domain-based pair natural orbital correlation DLPNO-CCSD(T) calculations along with the Symmetry-Adapted Perturbation Theory [SAPT(DFT)] applied to a cluster model. Next, using the DFT-D3 treatment with a periodic slab model, we analyze the interaction energies of the atomic silver clusters with the TiO2(110) surface. Finally, the hybrid HSE06 functional and a reduced density matrix treatment are applied to obtain the projected electronic density of states and photo-absorption spectra of the TiO2(110) surface, with and without adsorbed silver clusters. Our results show the stability of the supported clusters, the enhanced light absorbance intensity of the material upon their deposition, and the appearance of intense secondary broad peaks in the near-infrared and the visible regions of the spectrum, with positions depending on the size and shape of the supported clusters. The secondary peaks arise from the photo-induced transfer of electrons from intra-band valence 5s orbitals of the noble-metal cluster to 3d Ti band states of the supporting material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...