Towards superlubricity in nanostructured surfaces: the role of van der Waals forces†
Abstract
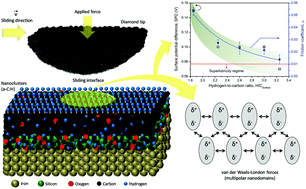
Hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H) thin films have a unique combination of properties that are fundamental in mechanical and electromechanical devices aimed at energy efficiency issues. The literature brings a wealth of information about the ultra-low friction (superlubricity) mechanism in a-C:H thin films. However, there is persistent controversy concerning the physicochemical mechanisms of contact mechanics at the atomic/molecular level and the role of electrical interactions at the sliding interface is still a matter of debate. We find that the hydrogenation of the outermost nanostructured surface atomic layers of a-C:H thin films is proportional to the surface potential and also to the friction forces arising at the sliding interface. A higher hydrogen-to-carbon ratio reduces the surface potential, directly affecting frictional forces by a less effective long-term interaction. The structural ultra-low friction (superlubricity) is attributed to a lower polarizability at the outermost nanostructured layer of a-C:H thin films due to a higher hydrogen density, which renders weaker van der Waals forces, in particular London dispersion forces. More hydrogenated nanodomains at the surface of a-C:H thin films are proposed to be used to tailor superlubricity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...