QM/MM studies on ozonolysis of α-humulene and Criegee reactions with acids and water at air–water/acetonitrile interfaces†
Abstract
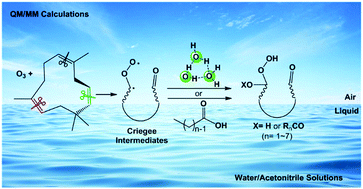
Herein, we employed combined CASPT2 and B3LYP electronic structure methods in the framework of the quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) approach to explore the ozonolysis of α-humulene and subsequent Criegee reactions with acids and water at the air–water/acetonitrile interface as a surrogate for atmospheric aqueous organic media. First, we found that the 1,3-cycloaddition reactions of ozone on α-humulene proceed concertedly and have small barriers (less than 2.5 kcal mol−1) at the QM(CASPT2)/MM level. Second, the five-membered ring cleavage reactions of the generated ozonides are rate-limiting steps and have considerable barriers (more than 10.0 kcal mol−1). These ring-opening reactions are also concerted and simultaneously lead to the cleavage of O–O and C–C bonds, producing sesquiterpene Criegee intermediates at the air–water/acetonitrile interface. Third, although these Criegee intermediates can react with water and acids near the air–water/acetonitrile boundary, the addition reactions with acids have smaller barriers, which range from 2.7 kcal mol−1 of R1-COOH to 5.6 kcal mol−1 of R7-COOH. In contrast, in water addition reactions, several different water-mediated reaction pathways have been disclosed. Their reaction barriers are found to decrease remarkably with an increase in the number of water molecules involved in the reactions. Finally, we found that in addition to low water concentration near the air–water/acetonitrile boundary, distinct reactivities of Criegee intermediates with acids and water play very important roles in the determination of the fates of the Criegee intermediates. Our present QM/MM study provides new mechanistic insights into ozonolysis and Criegee reactions at air–water/acetonitrile interfaces and gives important implications for new particle formation and secondary organic aerosol formation near the marine boundary.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...