A reversible conductivity modulation of azobenzene-based ionic liquids in aqueous solutions using UV/vis light†
Abstract
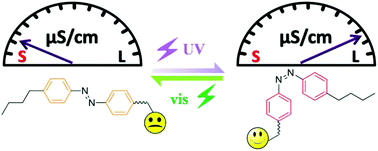
Photo-induced conductivity modulation of stimuli-responsive materials is of great importance from the viewpoint of fundamental research and technology. In this work, 5 new kinds of azobenzene-based photo-responsive ionic liquids were synthesized and characterized, and UV/vis light modulation of their conductivity was investigated in an aqueous solution. The factors affecting the conductivity modulation of the photo-responsive fluids, such as photo-isomerization efficiency, photo-regulation aggregation, concentration and chemical structure of the ionic liquids, were examined systematically. It was found that the conductivity of the ionic liquids in water exhibited a significant increase upon UV light irradiation and the ionic liquids with a shorter alkyl spacer in the cation showed a more remarkable photo-induced conductivity enhancement with a maximum increase of 150%. In addition, the solution conductivity was restored (or very close) to the initial value upon an alternative irradiation with visible light. Thus, the solution conductivity can be modulated using alternative irradiation with UV and visible light. Although the reversible photo-isomerization of the azobenzene group under UV/vis irradiation is the origin of the conductivity modulation, the photo-regulated aggregation of the ionic liquid in water is indispensable for the maximum degree of conductivity modulation because UV irradiation can weaken, even break the aggregated cis-isomers of the ionic liquids in an aqueous solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...