Interplay of proton and electron transfer to determine concerted behavior in the proton-coupled electron transfer of glutathione oxidation†
Abstract
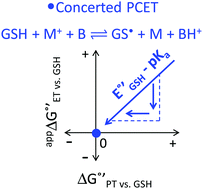
Glutathione (GSH), whose thiol group dictates its redox chemistry, is oxidized to the thiyl radical (GS˙), which rapidly dimerizes to GSSG. Previously, we found that the oxidation rate of GSH by IrCl62− depends on the base (B) concentration and the pKa of its conjugate acid BH+, so that collateral to a stepwise mechanism, the concerted pathway GSH + IrCl62− + B = GS˙ + IrCl63− + BH+ was proposed as the rate determining step. Herein, this investigation is extended to include oxidant-base pairs that render exothermic and endothermic conditions of ΔG°′ for electron transfer (ET) and proton transfer (PT). Experiments were conducted by the reaction of GSH with an electrogenerated oxidant M+ and using digital simulations to infer the mechanism. Data analysis shows that despite parallel mechanisms, the concerted one seems to predominate for the oxidant-base pair that renders the most isoenergetic coupled state, whereby a PT with 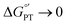 is capable of producing an ET with
is capable of producing an ET with 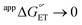 , as a result of the Nernstian shift of
, as a result of the Nernstian shift of 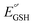 with pKa. In contrast, the stepwise PT–ET appears to dominate when GS− grows in stability as
with pKa. In contrast, the stepwise PT–ET appears to dominate when GS− grows in stability as 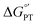 becomes more negative. Understanding the interplay between ET and PT will help in the design of catalysts for energy harvesting processes that rely on proton-coupled electron transfer.
becomes more negative. Understanding the interplay between ET and PT will help in the design of catalysts for energy harvesting processes that rely on proton-coupled electron transfer.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...