Ab initio conformational analysis of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline and the high-resolution rotational spectrum of its lowest energy conformer†
Abstract
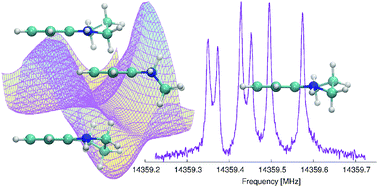
The saturated part of the 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline (THQ) molecule allows for the possibility of multiple conformers' existence. High-resolution microwave spectroscopy, supported by high-level quantum chemistry calculations, was used to determine the precise molecular structures of the conformers of THQ. Via the MP2 calculations, we were able to discriminate four stable conformations, i.e. two pairs of energetically equivalent enantiomorphic conformers. The results of the calculations also indicate that energetically non-equivalent conformers are separated by a low energy barrier (104 cm−1) that allows for conformational cooling to occur. The high resolution rotational spectrum with resolved hyperfine structure in the frequency range of 7–20 GHz was obtained using both the In-phase/quadrature-phase-Modulation Passage-Acquired-Coherence Technique (IMPACT) and the coaxially oriented beam resonator arrangement (COBRA) to perform Fourier transform microwave (FTMW) spectroscopy. The precise values of the rotational constants, 14N nuclear hyperfine coupling parameters and centrifugal distortion parameters were determined from the measured transition frequencies. Based on our experimental results, only the most stable enantiomeric pair of THQ contributes to the rotational spectrum under the conditions of our experiment as the less stable conformers seem to efficiently relax to the lower energy conformers. Thus the experimentally evaluated molecular constants unambiguously define the lowest energy conformer of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...