pH-Induced evolution of surface patterns in micelles assembled from dirhamnolipids: dissipative particle dynamics simulation
Abstract
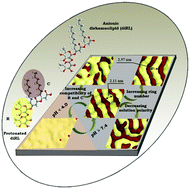
Dissipative particle dynamics (DPD) simulation is used to study the effect of pH on the morphological transition in micelles assembled from dirhamnolipids (diRLs), and analyze the pH-driven mechanism and influence factors of micellar surface patterns. At pH < 4.0, various multilayer structures with homogeneous surface patterns are observed, whereas diRLs can self-assemble into novel anisotropic morphologies with phase-separated surface patterns at pH > 7.4, such as patchy spherical micelles, rod-like micelles with helical surface patterns and a lamellar phase with anisotropic surface patterns. The change in a surface pattern results from the diverse molecular arrangement in the course of assembly due to the deprotonation of carboxyl groups. Further studies show that influence factors, such as molecular structure, solvent selectivity and intramolecular interaction, are closely associated with the changes in surface patterns and topological structures. In detail, decreasing the critical packing parameter of rhamnolipids, increasing the solution polarity and weakening the compatibility between rhamnose rings and alkyl chains are all beneficial to the formation of phase-separated surface patterns. Remarkably, a wider variety of surface patterns (randomly anisotropic surface patterns) can be further obtained with the different factors mentioned above. This work is expected to extend the applications of diRLs to advanced functional materials like drug delivery, optoelectronics and nanofiltration membranes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...