Cs-137 immobilization in C-S-H gel nanopores†
Abstract
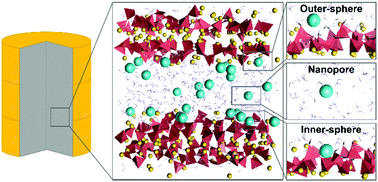
Cementation is a widespread technique to immobilize nuclear waste due to the low leachability of cementitious materials. The capacity of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H), the main component of cement, to retain radionuclide Cs has been empirically studied at the macroscale, yet the specific molecular scale mechanisms that govern the retention have not been determined. In this work, we employed molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the adsorption and diffusivity of Cs into a C-S-H gel nanopore. From the simulations, it was possible to distinguish three types of Cs adsorption configurations on the C-S-H: an inner-sphere surface site where Cs is strongly bound, an outer-sphere surface site where Cs is loosely bound, and Cs free in the nanopore. For each configuration, we determined the sorption energy, and the diffusion coefficients, up to two orders of magnitude lower than in bulk water due to the effect of nanoconfinement in the worst case scenario. It has also proved that Cs cannot displace the intrinsic Ca from the C-S-H surface, and we calculated the binding strength and the residence time of the cations in the surface adsorption sites. Finally, we quantified the average number of adsorption sites per nm2 of the C-S-H surface. All these results are the first insights into Cs retention in cement at the molecular scale and will be useful to build macroscopic diffusion models and devise cement formulations to improve radionuclide Cs retention from spent nuclear fuel.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...