Effects of crystal structure and composition on the photocatalytic performance of Ta–O–N functional materials
Abstract
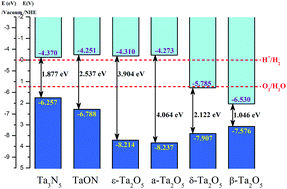
For photocatalytic applications, the response of a material to the solar spectrum and its redox capabilities are two important factors determined by the band gap and band edge position of the electronic structure of the material. The crystal structure and composition of the photocatalyst are fundamental for determining the above factors. In this article, we examine the functional material Ta–O–N as an example of how to discuss relationships among these factors in detail with the use of theoretical calculations. To explore how the crystal structure and composition influence the photocatalytic performance, two groups of Ta–O–N materials were considered: the first group included ε-Ta2O5, TaON, and Ta3N5; the second group included β-Ta2O5, δ-Ta2O5, ε-Ta2O5, and amorphous-Ta2O5. Calculation results indicated that the band gap and band edge position are determined by interactions between the atomic core and valence electrons, the overlap of valence electronic states, and the localization of valence states. Ta3N5 and TaON are suitable candidates for efficient photocatalysts owing to their photocatalytic water-splitting ability and good utilization efficiency of solar energy. δ-Ta2O5 has a strong oxidation potential and a band gap suitable for absorbing visible light. Thus, it can be applied to photocatalytic degradation of most pollutants. Although a-Ta2O5, ε-Ta2O5, and β-Ta2O5 cannot be directly used as photocatalysts, they can still be applied to modify conventional Ta–O–N photocatalysts, owing to their similar composition and structure. These calculation results will be helpful as reference data for analyzing the photocatalytic performance of more complicated Ta–O–N functional materials. On the basis of these findings, one could design novel Ta–O–N functional materials for specific photocatalytic applications by tuning the composition and crystal structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...