Lysine-based amino-functionalized lipids for gene transfection: the influence of the chain composition on 2D properties†
Abstract
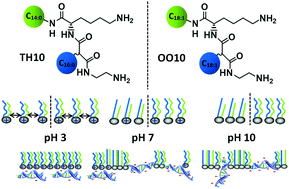
The influence of the chain composition on the physical–chemical properties will be discussed for five transfection lipids containing the same lysine-based head group. For this purpose, the chain composition will be gradually varied from saturated tetradecyl (C14:0) and hexadecyl (C16:0) chains to longer but unsaturated oleyl (C18:1) chains with double bonds in the cis configuration. In this work, we investigated the lipids as Langmuir monolayers at the air–water-interface in the absence and presence of calf thymus DNA applying different techniques such as infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy (IRRAS) and grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXD). The replacement of saturated tetradecyl (C14:0) and hexadecyl (C16:0) chains by unsaturated oleyl (C18:1) chains increases the fluidity of the lipid monolayer: TH10 < TT10 < OH10 < OT10 < OO10 resulting in a smaller packing density. TH10 forms the stiffest and OO10 the most fluid monolayer in this structure–property study. OO10 has a higher protonation degree compared to the saturated lipids TT10 and TH10 as well as to the hybrids OT10 and OH10 because of a better accessibility of the amine groups. Depending on the bulk pH, different scenarios of DNA coupling to the lipid monolayers have been proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...