Chemical-bond effect on epitaxial strain in perovskite sodium niobate†
Abstract
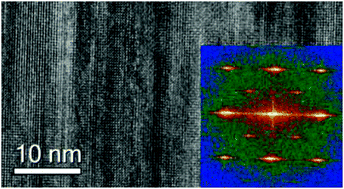
Epitaxial films and heterostructures of perovskite oxides attract tremendous scientific interest because of the unique phenomena therein. Especially important is the epitaxial growth of films subjected to substrate-induced misfit strain. We show here that in contrast to conventional misfit-controlled epitaxy, chemical bonds determine the crystal stability and strain in epitaxial films of sodium niobate on different cubic substrates. Strain relaxation in sodium niobate is independent of misfit magnitude and proceeds through perovskite-specific tilting of oxygen octahedra in addition to common defect formation. The observed structural relaxation evidences a major role of a large internal strain that originates from chemical bonds in the perovskite cell. The effect of chemical bonds on film strain is anticipated to also control the epitaxy of other perovskite oxides and related compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...