Fluorescence imaging of antibiotic clofazimine encapsulated within mesoporous silica particle carriers: relevance to drug delivery and the effect on its release kinetics†
Abstract
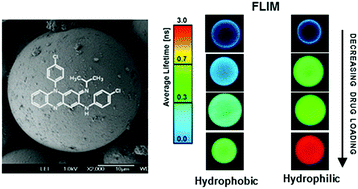
We report on the encapsulation of the antibiotic clofazimine (CLZ) within the pores of mesoporous silica particles having hydrophilic (CBET value of 137) and more hydrophobic (CBET value of 94 after calcination at 600 °C) surfaces. We studied the effect of pH on the released amount of CLZ in aqueous solutions and observed a maximum at pH 4.1 in correlation with the solubility of the drug. Less release of the drug was observed from the more hydrophobic particles which was attributed to a difference in the affinity of the drug to the carrier particles. Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy, emission spectra, and fluorescence lifetimes of single drug loaded particles provided detailed understanding and new knowledge of the physical form of the encapsulated drug and the distribution within the particles. The distribution of CLZ within the particles was independent of the surface chemistry of the particles. The confirmation of CLZ molecules as monomers or aggregates was revealed by controlled removal of the drug with solvent. Additionally, the observed optical “halo effect” in the fluorescent images was interpreted in terms of specific quenching of high concentration of molecules. The emission lifetime experiments suggest stronger interaction of CLZ with the more hydrophobic particles, which is relevant to its release. The results reported in this work demonstrate that tuning the hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of mesoporous silica particles can be used as a tool to control the release without impacting their loading ability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...