Rydberg transitions as a probe for structural changes and phase transition at polymer surfaces: an ATR-FUV-DUV and quantum chemical study of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and its nanocomposite with graphene†
Abstract
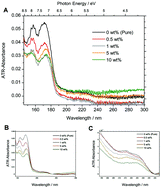
We investigated the surface (<50 nm) of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) and its nanocomposite with graphene by attenuated total reflection far- and deep-ultraviolet (ATR-FUV-DUV; 145–300 nm; 8.55–4.13 eV) spectroscopy and quantum mechanical calculations. The major absorption of polymers occurs in FUV and is related to Rydberg transitions. ATR-FUV-DUV spectroscopy allows for direct measurements of these transitions in the solid phase. Using ATR-FUV-DUV spectroscopy, periodic density functional theory (DFT) and time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT), we explained the origins of the FUV-DUV absorption of PHB and provided insights into structural changes of PHB which occur upon formation of a graphene nanocomposite and upon heating of the pure polymer. The structural changes cause specific and gradual spectral variations in FUV-DUV. We systematically studied the relaxation of the polymer helix and concluded that the common feature of all models of the unfolded helix lies in a specific and consistent FUV-DUV spectral signature. Relaxed structures feature a blue-shift of the major FUV transition (non-bonding molecular orbital to Rydberg 3p and π to π*) as compared with crystalline PHB. The FUV absorption of the relaxed structures was determined to be significantly stronger than that of the crystalline state. These results are consistent with the observed temperature-dependent spectra of the pure PHB. The simulation of the thermal expansion of the crystalline polymer by a periodic-DFT study allows us to exclude the possibility that spectral variations observed experimentally are influenced by changes in the crystalline phase. We concluded that the crystallinity of PHB at the sample surface increases with an increase in graphene content in the nanocomposite. However, it is unlikely that the polymer structure inside the crystal is affected; instead the FUV-DUV spectral variations result from changes in the polymer morphology that occur at the sample surface. The phase transition of PHB is affected by temperature and addition of graphene content. These changes are likely to be the opposite of those occurring in the bulk sample.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...