Computational exploration of Fe55@C240-catalyzed Fischer–Tropsch synthesis†
Abstract
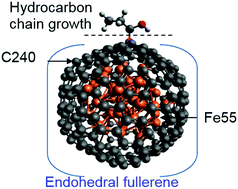
Single-shell carbon-encapsulated iron nanoparticles (SCEINs), Fe@C, have been shown to be charge-transfer complexes that can act as effective catalysts in the hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. A new generation of Fe-based catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS) which resembles SCEINs, e.g. single carbide nanoparticles encapsulated in carbon shells, has demonstrated enhanced activity and stability for FTS as compared to other carbon-supported Fe-based FTS. Thus the catalytic ability of SCEINs for the water splitting reactions and the Fe-based FTS catalyst with SCEINs-like features stimulated our exploration of SCEINs-catalyzed FTS. We performed ab initio DFT calculations using a realistic SCEINs model system Fe55@C240 to investigate for the first time the adsorption of the main reactants in FTS (CO and H/H2) and further to evaluate the catalytic ability of Fe55@C240 by reproducing the key steps of the well-known Fe-based FTS mechanisms (carbide, enol and CO insertion). Our calculations revealed: (i) a determinant role of Fe in enhancing CO adsorption (ii) strong cooperative effects with the adsorbates that stabilize the binding (iii) a less favourable two-sites reaction on Fe55@C240 due to preferential positions of the reactants farther to each other which prevent enol and carbide FTS mechanisms. We propose therefore a possible CO insertion path for hydrocarbon growth on Fe55@C240.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...