The influence of like-charge attraction on the structure and dynamics of ionic liquids: NMR chemical shifts, quadrupole coupling constants, rotational correlation times and failure of Stokes–Einstein–Debye†
Abstract
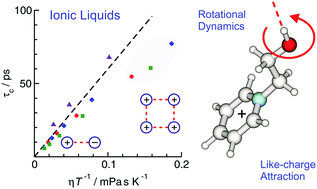
Ion pairing is one of the most fundamental atomic interactions in chemistry and biology. In contrast, pairing between like-charged ions remains an elusive concept. So far, this phenomenon was observed only for large-scaled structures, assemblies, stabilizing frameworks, or in aqueous solution wherein like-charge attraction is supported by mediating water molecules. Recently, we reported the formation of cationic clusters in pure ionic liquids (ILs) which all include hydroxyl groups (OH) for possible hydrogen bonding. In such structures like-charge repulsion is overcome by cooperative hydrogen bonds. The vibrational bands in the OH-stretch region of the infrared spectra can be clearly assigned to H-bonded ion pairs (c–a) or to H-bonded cationic clusters (c–c). The equilibrium between both types of ionic clusters can be controlled by using the same cation but differently strong interacting anions. In the present work, we study the influence of the cationic cluster formation on structural and dynamical NMR properties of ionic liquids, where we know that they form cationic clusters to different extent. First, we measure proton chemical shifts, δ1H, and determine deuteron quadrupole coupling constants, χD, from a calculated relation between both NMR properties. Reliable χD values for the liquid phase are a prerequisite for calculating reorientational correlation times, τOH, from measured deuteron relaxation times, T1. It is shown that the correlation times are significantly influenced by the amount of cationic clusters present in the IL. The Stokes–Einstein–Debye (SED) relation is valid for the ILs wherein H-bonded ion pairs (c–a) are the dominant species. With increasing cationic cluster (c–c) formation of e.g. cyclic tetramers, SED breaks down because of the structural heterogeneities.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...