Fine-structure transitions of interstellar atomic sulfur and silicon induced by collisions with helium†
Abstract
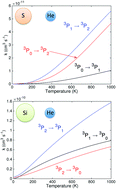
Atomic sulfur and silicon are important constituents of the interstellar matter and are both used as tracers of the physical conditions in interstellar shocks and outflows. We present an investigation of the spin–orbit (de-)excitation of S(3P) and Si(3P) atoms induced by collisions with helium with the aim to improve the determination of atomic sulfur and silicon abundances in the interstellar medium from S and Si emission spectra. Quantum-mechanical calculations have been performed in order to determine rate coefficients for the fine-structure transitions in the 5–1000 K temperature range. The scattering calculations are based on new highly correlated ab initio potentials. The theoretical results show that the (de-)excitation of Si is much faster than that of S. The rate coefficients deduced from this study are in good agreement with previous experimental and theoretical findings despite some deviations at low temperatures. From the computation of critical densities defined as the ratios between Einstein coefficients and the sum of the relevant collisional de-excitation rate coefficients, we show that local thermodynamic equilibrium conditions are not fulfilled for analyzing S and Si emission spectra observed in the interstellar medium. Hence, the present rate coefficients will be extremely useful for the accurate determination of interstellar atomic sulfur and silicon abundances.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Theory, experiment, and simulations in laboratory astrochemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...