Permeation pathways through lateral domains in model membranes of skin lipids†
Abstract
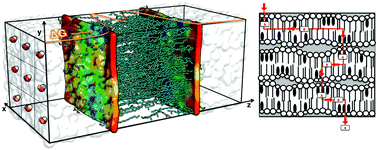
An understanding of how molecules permeate the complex lipid matrix of the stratum corneum (SC) skin barrier is important for transdermal drug delivery, preventing the adsorption of toxic chemicals and tackling skin diseases. In this paper we present atomistic molecular dynamics simulations of skin-lipid bilayers composed of ceramides, cholesterol (CHOL) and free fatty acids at different lipid compositions and levels of hydration and investigate both perpendicular and lateral permeation pathways through the systems. We show that in fully hydrated bilayers the lipids are heterogeneously distributed, with CHOL-rich domains emerging spontaneously during the simulations. Potential of mean constraint force calculations reveal that the most favourable permeation pathway for water in the direction normal to the bilayer is through a CHOL-rich region, probably due to the disordering effect of CHOL on lipids in the gel-phase. In systems with a low water content (akin to real skin) we find that rather than forming continuous layers, water forms flattened ellipsoid-shaped pools between the lipid headgroups, which are separated by dry regions. This implies that there is no continuous aqueous lateral pathway in the SC and may help to explain why skin is such an effective barrier. We propose that the most probable permeation pathway for a small polar molecule consists of hopping from the headgroup region of one bilayer to the next via a dry region, followed by permeation along the bilayer normal through a CHOL-rich region to the centre of the bilayer where it can diffuse laterally in the lower-density lipidic environment before encountering another CHOL-rich region through which it can exit the bilayer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...