Phosphine-free synthesis and optical stabilities of composition-tuneable monodisperse ternary PbSe1−xSx alloyed nanocrystals via cation exchange†
Abstract
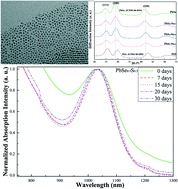
Compared to binary PbSe or PbS nanocrystals (NCs), ternary PbSe1−xSx alloyed NCs have unique electronic and optical properties such as high quantum efficiency, narrow band edge, and fast response time, and are widely used in infrared optoelectronic devices. In this work, high-quality composition-tunable monodisperse ternary PbSe1−xSx alloyed NCs were synthesized by employing cation exchange from host CdSe1−xSx alloyed NCs, which were pre-fabricated by using cadmium oxide, myristic acid and 1-octadecene (ODE) solutions of selenium/sulphur powders (Se/S-ODE), excluding toxic phosphine-containing solvents. The alloyed nature of PbSe1−xSx NCs was confirmed using powder X-ray diffraction (XRD). XRD patterns and field emission transmission electron microscopy (FETEM) images demonstrated that the average diameters of the resulting PbSe1−xSx alloyed NCs were not more than 5 nm, and ultraviolet-visible-near infrared (UV-vis-NIR) absorption spectra indicated that the NC size, hence the band gap, bared a linear relationship with the first absorption peak position. The temporal evolution of the absorption spectra revealed that the PbSe1−xSx alloyed NCs were air-stable due to the hybrid surface passivation of Cl− and Cd2+. X-ray fluorescence results indicated that slight stoichiometric deviations of PbSe1−xSx NCs occurred but never exceeded 15% of the expected composition, based on the amount of introduced hosts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...