Synthesis, X-ray crystallography, thermogravimetric analysis and spectroscopic characterization of isostructural one-dimensional coordination polymers as sorbents for some anions†
Abstract
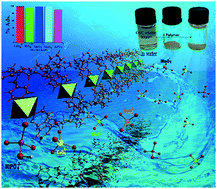
A new diaza-macrocyclic ligand bearing two pyridine side arms (L2) was synthesized and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (SCXRD), elemental analysis, FT-IR, and 1H and 13C NMR methods. The macrocyclic ligand showed a great tendency to act as an appropriate tecton in the formation of coordination polymers in the presence of Cu, Ni, Mn, Pb, and Cd chlorides. Five new isostructural one dimensional metal–organic coordination polymers [{M(Cl)2}(L)4] (M = Cu, Ni, Mn, Pb, Cd) were prepared in DMSO or DMF and characterized by elemental analysis, IR spectroscopy, TGA-DTG, powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. All of the polymers were employed as solid sorbents for Cr(VI) anions in aqueous solution. Within the series, the Pb(II) coordination polymer demonstrated notable absorption behavior for sorption of Cr(VI) and some oxo-anions such as MoO42−, WO42−, and MnO4− (environmental concern anions), together with HPO42−. The anion adsorption properties were attributed to the presence of surface positive charge on the coordination polymer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...