A novel exonuclease-assisted isothermal nucleic acid amplification with ultrahigh specificity mediated by full-length Bst DNA polymerase†
Abstract
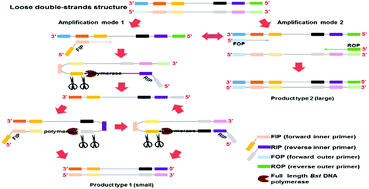
Here, we introduced a novel exonuclease-assisted isothermal nucleic acid amplification (Exo-NAT) utilizing the full-length Bst DNA polymerase combined with a melting curve analysis. This method achieved an ultrahigh specificity with a good detection limit (102 copies) in both singleplex and multiplex detection, which was validated by detecting three diarrhea-inducing pathogens, rotavirus A, astrovirus, and adenovirus, in 42 clinical samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...