Photocatalytic H2 production by dirhodium(ii,ii) photosensitizers with red light
Abstract
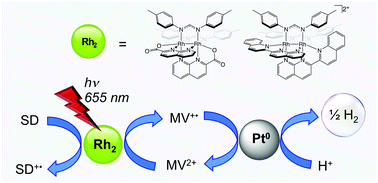
Photocatalytic proton reduction to generate H2 was achieved with the photosensitizers Rh2(DTolF)2(npCOO)2 (DTolF = p-ditolylformamidinate; npCOO− = 2-carboxylate-1,8-naphthyridine; 1) and [Rh2(DTolF)2(qnnp)2][BF4]2 (qnnp = 2-(quinolin-2-yl)-1,8-naphthyridine; 2) using a relay system containing the sacrificial donor BNAH (1-benzyl-1,4-dihydronicotinamide), electron acceptor MV2+ (methylviologen), and Pt nanoparticles as the catalyst with 655 nm irradiation. Comparison of the H2 evolution under similar experimental conditions show comparable activity of the Rh2(II,II) complexes (λirr = 655 nm) to that of the prototypical [Ru(bpy)3]2+ (bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine; 3) with λirr = 447 nm. This work demonstrates the ability of the new panchromatic Rh2(II,II) complexes to achieve photocatalysis with red light.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...