P–C reductive elimination in Ru(ii) complexes to convert triarylphosphine ligands into five- or six-membered phosphacycles†
Abstract
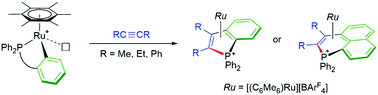
Rare examples of P–C reductive elimination in ruthenium complexes to generate phosphonium salts are presented. Triarylphosphines are converted into benzophospholium or phosphaphenalenium ligands via cyclometalation and 1,2-insertion of an alkyne followed by P–C reductive elimination. The intermediate in each step was successfully characterized using NMR and X-ray diffraction studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...