Size-dependent uptake of electrically neutral amphipathic polymeric nanoparticles by cell-sized liposomes and an insight into their internalization mechanism in living cells†
Abstract
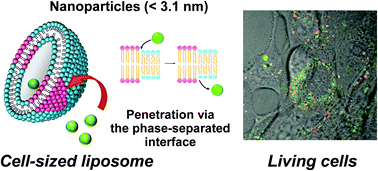
Size-dependent uptake behaviors of electrically neutral amphipathic polymeric nanoparticles in cell-sized liposomes and living cells were investigated. Kinetic analyses and the particle size distribution suggested a size-dependent penetration mechanism (size threshold: 3.1 nm). The definite size-dependent uptake provides a new insight into the interactions between nanomaterials and living cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...