Staudinger reaction using 2,6-dichlorophenyl azide derivatives for robust aza-ylide formation applicable to bioconjugation in living cells†
Abstract
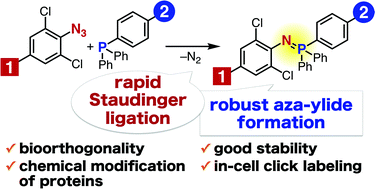
Efficient formation of water- and air-stable aza-ylides has been achieved using the Staudinger reaction between electron-deficient aromatic azides such as 2,6-dichlorophenyl azide and triarylphosphines. The reaction proceeds rapidly and has been successfully applied to chemical modification of proteins in living cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...