Scaffold mediated gene knockdown for neuronal differentiation of human neural progenitor cells†
Abstract
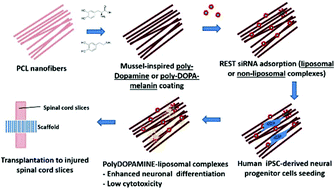
The use of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitor cells (hiPSC-NPCs) is an attractive therapeutic option for damaged nerve tissues. To direct neuronal differentiation of stem cells, we have previously developed an electrospun polycaprolactone nanofiber scaffold that was functionalized with siRNA targeting Re-1 silencing transcription factor (REST), by mussel-inspired bioadhesive coating. However, the efficacy of nanofiber-mediated RNA interference on hiPSC-NPCs differentiation remains unknown. Furthermore, interaction between such cell-seeded scaffolds with injured tissues has not been tested. In this study, scaffolds were optimized for REST knockdown in hiPSC-NPCs to enhance neuronal differentiation. Specifically, the effects of two different mussel-inspired bioadhesives and transfection reagents were analyzed. Scaffolds functionalized with RNAiMAX Lipofectamine-siREST complexes enhanced the differentiation of hiPSC-NPCs into TUJ1+ cells (60% as compared to 22% in controls with scrambled siNEG after 9 days) without inducing high cytotoxicity. When cell-seeded scaffolds were transplanted to transected spinal cord organotypic slices, similar efficiency in neuronal differentiation was observed. The scaffolds also supported the migration of cells and neurite outgrowth from the spinal cord slices. Taken together, the results suggest that this scaffold can be effective in enhancing hiPSC-NPC neuronal commitment by gene-silencing for the treatment of injured spinal cords.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...