pH-Sensitive micelles with mitochondria-targeted and aggregation-induced emission characterization: synthesis, cytotoxicity and biological applications†
Abstract
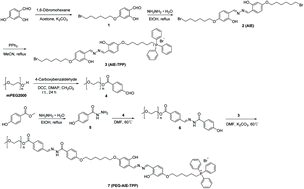
Subcellular organelle-specific reagents for simultaneous tumor targeting, imaging, and treatment are of enormous interest in cancer therapy. Herein, we present a mitochondria targeting micelle (PEG-AIE-TPP) by conjugating a triphenylphosphonium (TPP) with a fluorogen which can undergo aggregation-induced emission (AIE). At first, the in vitro and in vivo properties of the PEG-AIE-TPP micelle were characterized in detail. It was found that the micelle was reasonably stable at physiological pH and highly sensitive to mildly acidic pH stimuli. Importantly, this micelle could selectively localize and accumulate in the mitochondria, thus generating an aggregation-induced emission (AIE) effect as confirmed by the green fluorescence. Additionally, the micelle exhibited selective cytotoxicity to cancer cells and negligible toxicity to normal cells in vitro. The in vivo imaging and ex vivo imaging results showed that the accumulation tendency of the micelle at the tumor region was obvious. We also further proved the biocompatible, tumor targeting ability and antitumor activity of the PEG-AIE-TPP micelle in MCF-7 tumor-bearing mice. Accordingly, this mitochondria-targeted therapeutic micelle with good stability, biocompatibility, and tumor-targeting and antitumor activity provides a potentially unique tumor-targeted system for cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...