Short-term urea cycle inhibition in rat liver cells induced by polyethylene glycol†
Abstract
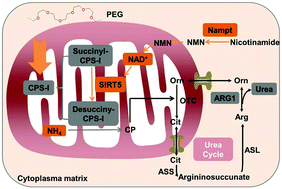
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is widely used in the biomedical field due to its outstanding properties. There are plenty of reports on the safety of PEG, but they are mostly restricted to its pharmacokinetic behaviour and pathological effect in vivo, and fail to elucidate its biological effects on cells at the molecular level. Consequently, here we illuminate the biological effect of PEG on a specific cellular pathway. We found that PEG could induce short-term urea cycle inhibition in rat liver cells in vitro without damaging the mitochondria and cells, which was proven to be an adaptive and reversible response to PEG at the molecular level. PEG could also induce a transient hepatic stress response in vivo, which was closely related with the urea cycle disorder. As a mechanistic study on the interactions between a synthetic biomedical polymer and cells at the molecular level, our work provides novel insights into the biological effects of polymers on a cellular system and is fundamental to the development of biomedical polymers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...