Scaffold-free three-dimensional cell culturing using magnetic levitation
Abstract
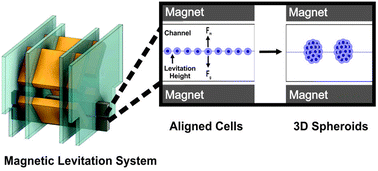
Three-dimensional (3D) cell culture has emerged as a pioneering methodology and is increasingly utilized for tissue engineering, 3D bioprinting, cancer model studies and drug development studies. The 3D cell culture methodology provides artificial and functional cellular constructs serving as a modular playground prior to animal model studies, which saves substantial efforts, time and experimental costs. The major drawback of current 3D cell culture methods is their dependency on biocompatible scaffolds, which often require tedious syntheses and fabrication steps. Herein, we report an easy-to-use methodology for the formation of scaffold-free 3D cell culture and cellular assembly via magnetic levitation in the presence of paramagnetic agents. To paramagnetize the cell culture environment, three different Gadolinium(III) chelates were utilized, which led to levitation and assembly of cells at a certain levitation height. The assembly and close interaction of cells at the levitation height where the magnetic force was equilibrated with gravitational force triggered the formation of complex 3D cellular structures. It was shown that Gd(III) chelates provided an optimal levitation that induced intercellular interactions in scaffold-free format without compromising cell viability. NIH 3T3 mouse fibroblasts and HCC827 non-small-cell lung cancer cells were evaluated via the magnetic levitation system, and the formation of 3D cell culture models was validated for both cell lines. Hereby, the developed magnetic levitation system holds promises for complex cellular assemblies and 3D cell culture studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...