Predicting the binding affinities of compound–protein interactions by random forest using network topology features†
Abstract
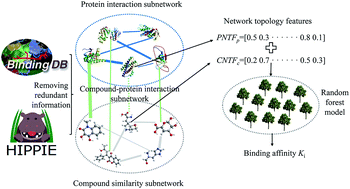
The identification of the binding affinity between a compound and a protein is of extraordinary significance to modern pharmacology and drug discovery. Despite the advances in experimental technology, the determination of binding affinity at the proteome scale is still expensive, laborious and time-consuming. Therefore, there is a strong desire for the development of a novel theoretical method for identifying the binding affinity of a compound and protein. A comprehensive node- and edge-weighted network is constructed comprising three subnetworks, namely compound–compound similarity, protein–protein interactions and compound–protein interactions. Based on the graph theory, some novel network topological features are proposed to characterize compound–protein interactions, and random forest is utilized to construct a model for predicting the binding affinity of each interaction. The Spearman and Pearson correlation coefficients of 0.8547 and 0.8779 as well as the root mean square error of 0.8638 are obtained, indicating the effectiveness of the developed method. A total of 2102 potential chemical–protein interactions are identified associated with diseases, such as aromatase excess syndrome and immunodeficiency autosomal recessive. It is anticipated that the proposed method may become a powerful high-throughput virtual screening tool for drug research and development.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...