An electrochemical sensor based on Fe3O4@PANI nanocomposites for sensitive detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+†
Abstract
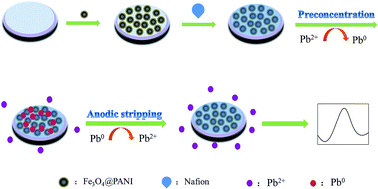
In this study, an easy-to-use electrochemical sensor was developed for the quantitative detection of lead ions (Pb2+) and cadmium ions (Cd2+). Core-shell ferroferric oxide@polyaniline (Fe3O4@PANI) nanoparticles were used as a sensitive platform for the detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+. Fe3O4 with large specific surface area could increase the sensitivity for detection. PANI as a conductive polymer with excellent electronic conductivity not only improved the electron transport speed in the detection process, but also produced good chelation with heavy ions. PANI contains a large number of amino and imino groups on its surface, thereby improving the detection sensitivity. Under optimal experimental conditions, the linear range for the detection of Pb2+ was from 0.1 to 104 nmol L−1; the detection limit was 0.03 nmol L−1, error limit of LOD was 1.1% and LOQ was 0.09 nmol L−1. The calculated LOD value of Cd2+ was 0.3 nmol L−1, the error limit of LOD was 1.5%, and LOQ was 0.9 nmol L−1. The prepared electrochemical sensor presented high sensitivity, good specificity and excellent stability; also, it is simple and easy to operate. This analysis strategy has a huge application prospect in the detection of other heavy metal ions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...