Magnetic deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction for determination of hexanal and heptanal in edible oils followed by gas chromatography–flame ionization detection†
Abstract
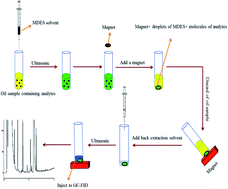
Use of a novel magnetic deep eutectic solvent (MDES), consisting of the inexpensive and simple components [choline chloride/para-cresol] [FeCl4] was examined using ultrasound-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction and back-extraction methods to determine hexanal and heptanal in edible oils. The MDES was specified using vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR), CHN elemental analysis, as well as Raman and Fourier-transform-infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Effective factors, including the volume of back-extraction solvent (μL), MDES (μL) volume, as well as extraction and back-extraction times (min) were optimized through a Box–Behnken design. Under optimal conditions, the calibration graphs of both analytes were linear at 0.05–100 mg L−1, with correlation coefficients >0.999. The limit of detection and limit of quantification was 19–25 μg L−1 and 63–83 μg L−1, respectively. This method was used to determine target analytes in spiked samples of edible oils; the relative mean recovery ranged from 94% to 102%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...