A sulfonated chitooligosaccharide modified silica material for hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and its chromatographic evaluation†
Abstract
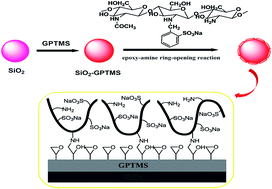
A novel stationary phase derived from a sulfonated chitooligosaccharide (COS) was prepared and evaluated in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) mode. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), elemental analysis (EA), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) supported the successful immobilization of the obtained material. The effects of various parameters including the composition of the mobile phase, buffer concentration, buffer pH, column temperature, and stability on the retention behavior of the stationary phase were investigated by using nucleosides and bases. Two empirical models, partitioning and adsorption, were used to describe the separation mechanism of the stationary phase. The corresponding column could also successfully separate other polar and hydrophilic compounds such as water-soluble vitamins, salicylic acid related compounds, and melamine. The newly synthesized stationary phase displayed potential for application in HILIC mode separation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...